miércoles, 16 de diciembre de 2015
Plants: annual and perennial
lunes, 30 de noviembre de 2015
Invertebrates: Arthropods
Arthropods: they have an external skeleton , jointed legs and a segmented body.
The easiest way to distinguish an arthropod from any other animal is to see if they have:

The easiest way to distinguish an arthropod from any other animal is to see if they have:
1) A segmented body.
This means that they will have a body made up of more than one part. Spiders have two segments and flies have three segments.
2) Many jointed legs or limbs.
Spiders have 8 legs, millipedes can have... Hundreds!
3) An exoskeleton.
This is an external skeleton. Like armor, it protects the arthropods body. When arthropods are born the exoskeleton is soft but hardens quickly and it can be shed as the creature grows. Arthropods are invertebrates; which means that they do not have a backbone.
4) Cold blooded
Arthropods are cold blooded -- which means, their body temperature depends on the temperature of the environment surrounding them.
They include insects, arachnids, crustaceans and myriapods.
- Insects:
- Insect bodies have three parts, the thorax, abdomen and head.
- Insects have two antennae.
- Insects have three pairs of legs.

- Arachnids:
- Arachnids bodies have two parts.
- Arachnids do not have antennae. They do not have wings.
- Arachnids have eight legs.

- Crustaceans:
- They have got 4 antennae.

- Myriapods:
They have got many legs

They have got many legs

Invertebrate: molluscs
Molluscs are a large group of invertebrate animals. Molluscs have soft bodies, and their bodies are not divided into rings like the segmented worms called annelids . Molluscs don't have legs, though some have flexible tentacles for sensing their environment or grabbing things. Most mollusc species grow a hard shell for protection, but their shell grows in only one or two pieces. It doesn't have joints like the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans .
There are three main groups of molluscs.
1)Snails ( Gastropoda (gas′trə pod′), ) are the most diverse group, there are tens of thousands of species. Nearly all snails grow a spiral shell that is all one piece. A few snail groups have stopped growing shells; they're called slugs .

2) Bivalvia (/ˈbaɪˌvælv/ ) , the clams, oysters, and mussels . These are molluscs with two shells that they can close up tight for protection.

3)Cephalopoda (sef′ə lə pod′) , the squids and octopuses. They only live in salt water. They have no shells, but are larger, smarter, and faster than their relatives in the other groups. Squids and octopuses are all predators; they eat fish, crustaceans, and other mollusks.
jueves, 26 de noviembre de 2015
Invertebrates
Sponges are very simple animals that live permanently attached to a location in the water.
The body of this animal has thousands of pores which let water flow through it continually. Sponges obtain nourishment and oxygen from this flowing water. The flowing water also carries out waste products.
Suck the water in, filter out the food, and send the water out.
These invertebrates range in size from a few millimeters to 2 meters tall.
Cnidarians : they have soft bodies with tentacles to catch their prey. Some can move about ( jellyfish); others are attached to surfaces beneath the sea (coral).

Echinoderms are marine animals. They have an internal skeleton made up of plates. Many echinoderms have spines.

If you ever turn a starfish over you will see hundreds of little tubes on each arm. Those tubes attach to an object, suck in, and attach to help the creature move.
Worms have long, soft bodies. They do not have legs. Some worms are terrestrial and some are aquatic.








Arthropods:

If you ever turn a starfish over you will see hundreds of little tubes on each arm. Those tubes attach to an object, suck in, and attach to help the creature move.
Worms have long, soft bodies. They do not have legs. Some worms are terrestrial and some are aquatic.
Molluscs are a large group of invertebrate animals. Molluscs have soft bodies, and their bodies are not divided into rings like the segmented worms called annelids . Molluscs don't have legs, though some have flexible tentacles for sensing their environment or grabbing things. Most mollusc species grow a hard shell for protection, but their shell grows in only one or two pieces. It doesn't have joints like the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans .
There are three main groups of molluscs.
1)Snails ( Gastropoda (gas′trə pod′), ) are the most diverse group, there are tens of thousands of species. Nearly all snails grow a spiral shell that is all one piece. A few snail groups have stopped growing shells; they're called slugs .

2) Bivalvia (/ˈbaɪˌvælv/ ) , the clams, oysters, and mussels . These are molluscs with two shells that they can close up tight for protection.

3)Cephalopoda (sef′ə lə pod′), the squids and octopuses. They only live in salt water. They have no shells, but are larger, smarter, and faster than their relatives in the other groups. Squids and octopuses are all predators; they eat fish, crustaceans, and other mollusks.
Arthropods:
The easiest way to distinguish an arthropod from any other animal is to see if they have:

1) A segmented body.
This means that they will have a body made up of more than one part. Spiders have two segments and flies have three segments.
2) Many jointed legs or limbs.
Spiders have 8 legs, millipedes can have... Hundreds!
3) An exoskeleton.
This is an external skeleton. Like armor, it protects the arthropods body. When arthropods are born the exoskeleton is soft but hardens quickly and it can be shed as the creature grows. Arthropods are invertebrates; which means that they do not have a backbone.
4) Cold blooded
Arthropods are cold blooded -- which means, their body temperature depends on the temperature of the environment surrounding them.
Invertebrates: Echinoderms.
Echinoderms are marine animals. They have an internal skeleton made up of plates. Many echinoderms have spines.

If you ever turn a starfish over you will see hundreds of little tubes on each arm. Those tubes attach to an object, suck in, and attach to help the creature move.

If you ever turn a starfish over you will see hundreds of little tubes on each arm. Those tubes attach to an object, suck in, and attach to help the creature move.
Invertebrates: Worms
Worms have long, soft bodies. They do not have legs. Some worms are terrestrial and some are aquatic.

Invertebrates: Cnidarians
Cnidarians : they have soft bodies with tentacles to catch their prey. Some can move about ( jellyfish); others are attached to surfaces beneath the sea (coral).





martes, 24 de noviembre de 2015
Invertebrates: Sponges
Sponges are very simple animals that live permanently attached to a location in the water.
The body of this animal has thousands of pores which let water flow through it continually. Sponges obtain nourishment and oxygen from this flowing water. The flowing water also carries out waste products.
Suck the water in, filter out the food, and send the water out.
These invertebrates range in size from a few millimeters to 2 meters tall.
lunes, 16 de noviembre de 2015
Health. Ampliación de la lección
martes, 10 de noviembre de 2015
The influence of the new forms of leisure on our health
martes, 20 de octubre de 2015
miércoles, 7 de octubre de 2015
jueves, 24 de septiembre de 2015
Excretory system
Excretory system- agrega2
1. Excretory system organs.
1.1 Excretion.
1.2 The excretory system.
1.3 Sweat glands.
2 How the kidney works.
2.1 The kidney
3 The skin
3.1 The skin function.
3.2 Test
4 The urination process
4.1 The urination process
4.2 The urinary system.
4.3 The kidneys and the urinary tracts.
Excretory system
1. Excretory system organs.
1.1 Excretion.
1.2 The excretory system.
1.3 Sweat glands.
2 How the kidney works.
2.1 The kidney
3 The skin
3.1 The skin function.
3.2 Test
4 The urination process
4.1 The urination process
4.2 The urinary system.
4.3 The kidneys and the urinary tracts.
Excretory system
Circulatory system
The human blood circulation system- agrega2
Arteries, veins and capillaries
The heart as a double pump-
Human circulation is double
Composition of the blood
White blood cells
Blood plasma
Drag each piece of the heart to the patient´s chest
Arteries, veins and capillaries
The heart as a double pump-
Human circulation is double
Composition of the blood
White blood cells
Blood plasma
Drag each piece of the heart to the patient´s chest
miércoles, 23 de septiembre de 2015
Probiotics
Los alimentos probióticos son alimentos con microorganismos vivos adicionados que permanecen activos en el intestinoy ejercen importantes efectos fisiológicos. Ingeridos en cantidades suficientes, pueden tener efectos beneficiosos, como contribuir al equilibrio de la microbiota intestinal del huésped y potenciar el sistema inmunitario. Pueden atravesar elAparato digestivo y recuperarse vivos en los excrementos, pero también se adhieren a la mucosa intestinal. No son patógenos, excepto en casos en que se suministran a individuos inmunodeficientes.
Contienen esta clase de microorganismos y, por tanto, son alimentos probióticos los yogures frescos y muchos otros productos lacto fermentados.
viernes, 18 de septiembre de 2015
Respiratory system
1.1 Respiratory system and its functions.
1.2. Join each part of the respiratory system to its function.
2.1 Inspiration and expiration
2.2. Fill in the gap
Presentation and game
Presentation and game (label the parts of the respiratory system).Librosvivos
Respiratory system Song
1.2. Join each part of the respiratory system to its function.
2.1 Inspiration and expiration
2.2. Fill in the gap
Presentation and game
Presentation and game (label the parts of the respiratory system).Librosvivos
Respiratory system Song
martes, 15 de septiembre de 2015
Nutrition
Digestive system. Presentation and game (label the different parts of the digestive system)
Digestive system + match
MATCH a number with the appropriate definition (letter):
1) Teeth
2) Oesophagus
3) Liver
4) Bile
5) Gallbladder
a) A sac attached to the liver in which bile is stored.
b) It produces bile.
c) It transports food from the mouth to the stomach.
d) They are used to chew food into small pieces.
e) It breaks down fats into small droplets.
Digestive system
Nutrition organs 6º
Digestive system + match
MATCH a number with the appropriate definition (letter):
1) Teeth
2) Oesophagus
3) Liver
4) Bile
5) Gallbladder
a) A sac attached to the liver in which bile is stored.
b) It produces bile.
c) It transports food from the mouth to the stomach.
d) They are used to chew food into small pieces.
e) It breaks down fats into small droplets.
Digestive system
Nutrition organs 6º
lunes, 14 de septiembre de 2015
Life processes
Three main life processes
Nutrition: Odd one out + classify (digestion, respiration, circulation and excretion)
domingo, 28 de junio de 2015
Human Reproductive System
Changes during puberty
Puberty

Read and then answer the test of your booklet
Organs of the female reproductive system
Fertilisation
Reproduction and pregnancy
Pregnancy
Stages of pregnancy
Birth
TEST
Puberty

Read and then answer the test of your booklet
Organs of the female reproductive system
Fertilisation
Reproduction and pregnancy
Pregnancy
Stages of pregnancy
Birth
TEST
miércoles, 3 de junio de 2015
Ramón y Cajal. Structure and function of the nervous system.
It was his work that established the ‘neuron doctrine’ as the accepted model for the structure and function of the nervous system, and our modern understanding of the nervous system is founded on this doctrine.
He studied tissue from different regions of the brain and from the brains of various species of vertebrates. He discovered that, rather than being fused together in a continuous web (as had previously been thought), the cells that make up the nervous system are in fact discrete units, separate from one another.
Cajal’s discovery that nerve cells were independent required a new model for how the nervous system functioned. He proposed that electrical impulses were conducted through chains of nerve cells and that the direction of conduction is fixed. This is the ‘Law of Dynamic Polarization’, which states that impulses are conducted in a fixed direction through the neuron from dendrites, through the cell body, to the axon.
Cajal received many honours, including the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1906, and the Spanish government built the Cajal Institute, for neurobiological research, in his name.
He studied tissue from different regions of the brain and from the brains of various species of vertebrates. He discovered that, rather than being fused together in a continuous web (as had previously been thought), the cells that make up the nervous system are in fact discrete units, separate from one another.
Cajal’s discovery that nerve cells were independent required a new model for how the nervous system functioned. He proposed that electrical impulses were conducted through chains of nerve cells and that the direction of conduction is fixed. This is the ‘Law of Dynamic Polarization’, which states that impulses are conducted in a fixed direction through the neuron from dendrites, through the cell body, to the axon.
Cajal received many honours, including the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1906, and the Spanish government built the Cajal Institute, for neurobiological research, in his name.
Etiquetas:
Human Body 5º,
Scientists and inventors
martes, 2 de junio de 2015
Alexander Graham Bell
Alexander Graham Bell
Reading comprehension: Read and answer the questions.
--> Copy the 9 questions and the appropriate answers in your notebook.
Reading comprehension: read and answer the questions.
--> Copy the questions and the appropriate answers in your notebook.
Reading comprehension
--> True or false. Write the True sentences in your notebook.
Reading comprehension: Read and answer the questions.
--> Copy the 9 questions and the appropriate answers in your notebook.
Reading comprehension: read and answer the questions.
--> Copy the questions and the appropriate answers in your notebook.
Reading comprehension
--> True or false. Write the True sentences in your notebook.
viernes, 29 de mayo de 2015
Nuclear energy: image of a nuclear reactor
jueves, 28 de mayo de 2015
miércoles, 20 de mayo de 2015
jueves, 16 de abril de 2015
miércoles, 15 de abril de 2015
miércoles, 8 de abril de 2015
jueves, 5 de marzo de 2015
Checking comprehension of the unit. 5th grade
1 What are two
goals when designing machines?
1
2 Modern cars
focus on….?
·
3 In what forms
can energy exist?
1
4 What happens
to energy when it is not at work? Give
an example.
·
5 Fill in the
blanks with the properties of energy:
Energy can be________ from one form to
another.
Energy can be________from one body to another.
Energy can be ________. Example: animals
_____food energy.
Energy can be_________from one place to
another.
6 What is a
renewable energy source? Give an
example.
·
7 What is a
non-renewable source? Give an example.
·
8 Fill in the
chart (if not applicable, put N/A)
|
Energy Source
|
Renewable or Non-Renewable?
|
Type of energy
|
It´s energy can be transformed into…
|
Fossil Fuels or Nuclear Fuels?
|
Does this energy source cause pollution?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 What are some
of the negative consequences of using energy to provide us with modern comfort?
What causes these environmental problems?
How do they effect the environment?
·
10 Which do you
think causes the greatest alarm for the environment? Why?
11 What are ways
we can save energy in our daily lives?
martes, 27 de enero de 2015
Investigate: LED Lighting
- Find out as much as you can about LED lighting.
a) Can it help us save energy?
b) Where can it be used?

a) Can it help us save energy?
b) Where can it be used?
Hydroelectric Power Plant
En español
viernes, 23 de enero de 2015
jueves, 22 de enero de 2015
Let´s talk about cars
1. Solar powered car, electric car, fuel car. What is a hybrid car?
2.What source of energy do they use? Compare them
viernes, 9 de enero de 2015
Refraction, prisms and lens
Refraction, prisms and lens



La Refracción de la luz



Refracción de la luz es el cambio de dirección que sufre la luz cuando pasa de una sustancia transparente a otra. Ejemplo, el aire, a otro, como el agua.
Los rayos de luz que cambian de dirección se llaman rayos refractados.


Al introducir una cuchara en un vaso con agua parece que se dobla o se corta, porque los rayos de luz se desvían, ya que viajan más lento al pasar del aire, donde existen menos partículas, al agua, donde hay más.
jueves, 8 de enero de 2015
What is an ecosystem? COMPONENTS, TYPES, NUTRITION, ORGANISATION,
1.Components
2. Types of ecosystems.
Read about the different types of natural ecosystems
3.Food chain - Nutrition in an ecosystem
Food chains. Read and play
Food chains and food webs
Food chain- Arctic Habitat
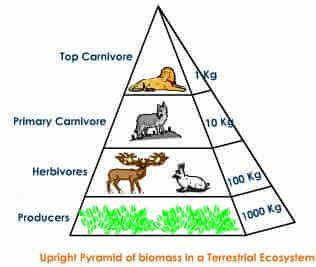
4. How do living things organise in an ecosystem?
individual, population, community and ecosystem- español


5 TERRESTRIAL ECOSYSTEMS
Tropical Rainforest
Cold desert
Taiga
Savannah
Mediterranean forest
Hot desert
** Ecosystems in Spain
Review: Ecosystems/ Food chains/ Parasitism, mutualism, competition / Dangers to the environment
Interesting exercices from other book
6 Marine ecosystem
En los ecosistemas marinos se distinguen distintas zonas ocupadas por seres vivos diferentes. La PROFUNDIDAD de las aguas es importante porque de ello dependen la LUZ y la TEMPERATURA y, por tanto, el tipo de organismos que se encuentran en estos ecosistemas.

2. Types of ecosystems.
Read about the different types of natural ecosystems
3.Food chain - Nutrition in an ecosystem
Food chains. Read and play
Food chains and food webs
Food chain- Arctic Habitat

4. How do living things organise in an ecosystem?
individual, population, community and ecosystem- español


Tropical Rainforest
Cold desert
Taiga
Savannah
Mediterranean forest
Hot desert
** Ecosystems in Spain
Review: Ecosystems/ Food chains/ Parasitism, mutualism, competition / Dangers to the environment
Interesting exercices from other book
6 Marine ecosystem
En los ecosistemas marinos se distinguen distintas zonas ocupadas por seres vivos diferentes. La PROFUNDIDAD de las aguas es importante porque de ello dependen la LUZ y la TEMPERATURA y, por tanto, el tipo de organismos que se encuentran en estos ecosistemas.

Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)